Get started with Grafana Loki¶
Grafana Loki is the default and preferred log aggregation system for all applications on the Nais platform. It's integrated with Grafana and inspired by Prometheus, providing a powerful and efficient way to store, search, and analyze your application logs.
Default logging with Grafana Loki¶
Grafana Loki is enabled by default for all Nais applications. Your application logs written to stdout and stderr are automatically collected and sent to Loki without any configuration required.
If you need to customize your logging destinations or add additional ones, you can explicitly configure them in your nais application manifest:
Default behavior
Loki is automatically used as the default destination. You only need to configure logging destinations if you want to:
- Add additional logging destinations alongside Loki
- Disable Loki logging (not recommended)
- Use custom logging configurations
Log sources
Loki collects logs that are written to stdout and stderr. Logs written to files or other log appenders such as team logs are handled separately.
Accessing your logs in Grafana¶
Grafana Loki is integrated directly with Grafana, providing multiple ways to access and analyze your logs:
Quick access via Logs Drilldown¶
Click on the "Logs Drilldown" link in the Grafana UI to access the dedicated logs interface, or navigate to the traditional "Explore" view and select one of the Loki data sources (one for each environment).
Adding logs to dashboards¶
You can add a Logs Panel to your Grafana dashboards for persistent log monitoring. See Adding logs to your Grafana dashboard for detailed instructions.
Getting started with logs (new to Grafana?)¶
If you're new to working with logs in Grafana, here's a step-by-step guide to get you started:
1. Navigate to Grafana Logs¶
- Open Grafana from your Nais tenant
- Click "Logs Drilldown" in the navigation or go directly to the Logs Drilldown interface
- Alternatively, use the traditional "Explore" view (compass icon) and select the appropriate Loki data source for your environment (dev-gcp, prod-gcp, etc.)
2. Find your application logs¶
Start with a simple query to find logs from your application:
{service_name="your-app-name", service_namespace="your-team"}
Replace your-app-name with your actual application name and your-team with your actual team name. This will show all logs from your application.
3. Search log content¶
To search for specific text within your logs:
{service_name="your-app-name", service_namespace="your-team"} |= "some-value"
This finds all logs containing the word "some-value".
4. Filter by log level¶
Many applications use structured logging with levels:
{service_name="your-app-name", service_namespace="your-team"} | detected_level="error"
Loki will automatically detect the log level if your application outputs structured logs.
5. Filter by structured log data¶
If your application outputs structured logs (e.g., JSON), you can filter by specific fields:
{service_name="your-app-name", service_namespace="your-team"} | json | some_field="some-value"
Using the query builder¶
For beginners, we recommend using the query builder mode when writing your first LogQL queries. The query builder provides a graphical interface that helps you build queries by selecting labels and fields from your logs.
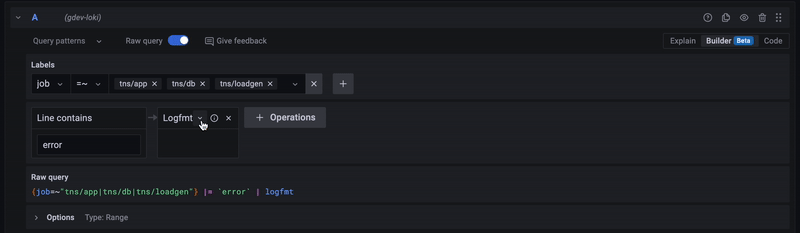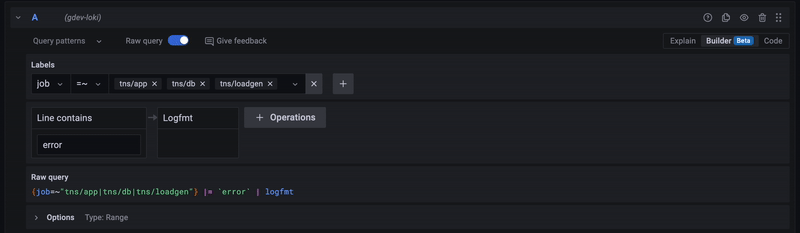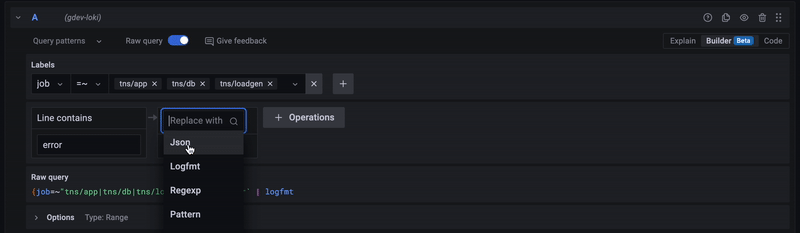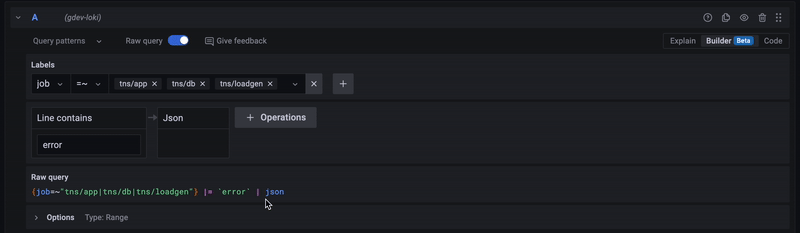
To enable query builder mode:
- Look for the "Builder/Code" toggle above the query input
- Select "Builder" mode
- Use the dropdown menus to select labels and operations
- Switch to "Code" mode to see the generated LogQL query
Understanding LogQL basics¶
Grafana Loki uses LogQL, a query language inspired by PromQL. Here are the key concepts:
- Log Stream Selectors: Use curly braces to select log streams:
{service_name="myapp", service_namespace="myteam"} - Filter Expressions: Use
|=for contains,!=for not contains:{service_name="myapp", service_namespace="myteam"} |= "some-value" - Regular Expressions: Use
|~for regex matches:{service_name="myapp", service_namespace="myteam"} |~ "some-value|another-value" - JSON Parsing: Use
| jsonto parse JSON logs and access fields:{service_name="myapp", service_namespace="myteam"} | json | some_field="some-value" - Time Ranges: Use the time picker in Grafana to limit your search to specific time periods
Common troubleshooting tips¶
No logs appearing?¶
- Check your application name: Ensure the
service_namelabel matches your actual application name in the manifest - Verify the namespace: Make sure you're searching in the correct
service_namespace - Check the time range: Expand the time range in Grafana's time picker
- Confirm log output: Ensure your application is writing logs to
stdoutorstderr
Too many logs?¶
- Add more specific filters: Use multiple labels to narrow down results
- Use time-based filtering: Select a smaller time window
- Filter by log level: Focus on specific log levels like
ERRORorWARN
Performance tips¶
- Use specific label selectors: Always include
service_nameandservice_namespacelabels when possible - Filter before parsing: Apply filters before using
| jsonto improve performance - Limit time ranges: Shorter time ranges perform better
- Use the query builder: It helps prevent syntax errors and suggests available labels
Next steps¶
Once you're comfortable with basic log viewing, explore these advanced features:
- Log aggregation: Count and group logs by different criteria
- Metrics from logs: Generate metrics from log data
- Alerting: Set up alerts based on log patterns
- Dashboard integration: Create comprehensive monitoring dashboards